The 6 Features of the Blockchain Technology
June 22, 2020
5 min

Introduction
Technologically speaking, a blockchain is a decentralized network that has a common shared memory (“status”) and updates its status by processing inputs (“transactions”) according to a set of prescribed rules (“the protocol”). This entire process is done without any kind of central coordination or single point of potential failure, instead, it is carried out by thousands of volunteers.
The Blockchain: a New Payment System
The blockchain is one of the most promising inventions in the field of information technology.
One of its greatest strengths is certainly its transversality: the innovation of the blockchain concerns the way in which a transaction is carried out, and transactions cover a multitude of sectors. The sector in which it already finds broad development, however, is the financial sector.
Despite the entire universe of possibilities it involves, the blockchain was born as payment technology. One of the most interesting use cases relates to the sending of units of value, often called “digital assets“. One of the most tested and developed digital assets is cryptocurrency. While still shrouded in mystery and suspicion for most people, cryptocurrencies are growing at a rapid pace and are entering our lives with the same speed.
The 6 Features of the Blockchain
Since Satoshi Nakamoto conceptualised Bitcoin as his first application in 2008, the blockchain has been in the spotlight. She is the real star of the bitcoin revolution.
The blockchain technology introduces a number of fundamental concepts that characterise it as innovative:
- Decentralisation. Unlike banking transactions, “on-chain” transactions are neither controlled nor mediated by banks and governments, in other words, they are not centralised. By removing the authority at the top, the decentralised system of the blockchain places new financial freedom in the hands of whoever uses it.
- No middlemen. Intermediaries such as payment services and banks guarantee the legitimacy of fiat currency transactions. Blockchain technology replaces these third parties with a data registry distributed to the entire community of participating volunteers. The trust, in this case, is placed in people or organisations that are equal to the user (peers) and no longer in a large faceless company.
- Transparency. All on-chain transactions are publicly visible. When it comes to digital assets, you can enter a transaction ID in a block explorer and see a transaction recorded on the blockchain. Each transaction ID is unique.
- Resistance to censorship. Governments and banks can, at their discretion, decide whether to block transactions and accounts. The blockchain model, on the other hand, is based on an agreed set of rules. All those who use the network are bound by the same set of rules, they share the same rights and duties.
- Immutability. Once recorded, a blockchain transaction cannot be changed or deleted. Transactions are irreversible, meaning that even in the unlikely event that a network is successfully hacked, existing transactions can never be cancelled.
- Security. The security of the blockchain depends on four factors: immutability, consensus algorithm, key cryptography and crypto-economics (mathematical behavioural and decision-making models). The integrity of cryptocurrency depends solely on the integrity of the blockchain.
The Blockchain Structure
The characteristics of the blockchain are derived from its structural components:
The Distributed Ledger. Transactions are made and recorded on the blockchain. The data for each transaction is recorded on a sort of giant ledger which is distributed among all the nodes of the network. Each node participating in the blockchain network controls each transaction. This ensures that no central authority is required to confirm blockchain transactions.
The Consensus Mechanism. When a sufficient number of nodes meet the consent for a transaction, the transaction is successfully confirmed. This is possible through special blockchain-specific algorithms.
Public Key Encryption. Public key encryption is used on the blockchain to encrypt data and create digital signatures. The public key can be shown to anyone, which is why it is called “public”. The private key, however, should only be known to the user to whom it belongs. This is the key that ensures that only the user has control over their digital resources. Whoever has the correct key pair can create a digital signature to confirm a transaction or decrypt any encrypted data. This is why your private key must remain secret.
Conclusion
The blockchain applies encryption to decentralised systems for the first time and equips itself with a compatible and native currency.
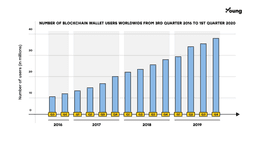
By bringing to light issues such as privacy, transparency and financial democracy, the blockchain is having a strong impact, especially on the payments sector. According to data from Statista.com, $2.9 billion was spent on the implementation of blockchain technology in 2019. At this rate, the global blockchain market is expected to grow to $60 billion by 2024. The impact of the blockchain is also clear from the fact that market giants such as IBM and Microsoft are competing for the most advanced solutions and a country like Australia is creating a national blockchain.