Flash Loans: How They’re Accelerating DeFi Lending
September 29, 2021
7 min
Flash loans are decentralised instant loans available on Aave. They mainly facilitate arbitrage strategies and are a still developing innovation in the DeFi sector.
Difference between flash loan and standard loan
A normal loan requires collateral.
In the traditional system, this collateral is your creditworthiness, and applying for a loan takes time and several requirements, such as:
- age between 18 and 70.
- a demonstrable income
- residence in the territory in which you are applying
- be an account holder at the credit institution from which the loan is being requested
Once the loan application is approved, the borrower can repay it with interest over a period of weeks, months or years.
DeFi loans, on the other hand:
- Do not require identity verification or proof of income
- Do not require a bank account
- They are instantaneous
- Decentralised and therefore global and without censorship or restrictions
- Require to deposit collateral covering more than 100% of the requested loan.
Flash loan is something else, again:
- Payoff occurs within seconds of issuance
- Do not require collateralisation
- Do not require interest, but only a fee
How a flash loan works
How is it possible that a flash loan is paid off immediately, and at the same time allows so many use cases?
Let’s start with the basics of how a blockchain transaction works.
A transaction consists of a series of operations, and is only confirmed if all these operations are successful. Otherwise, it is cancelled in its entirety.
A simple transaction of sending cryptocurrency from wallet A to wallet B requires 2 operations:
- Updating the balance of wallet A by subtracting cryptocurrencies
- Updating the balance of wallet B by adding cryptocurrencies
If the second operation fails, the first is also cancelled, and vice versa.
This is because the operations in the same transaction are indivisible, there is no one without the other, which is why they are called ‘atomic’.
A single transaction on Ethereum could even be:
- Operation 1: generate a DAI loan on Compound by depositing ETH
- Operation 2: Exchange 50% of DAI generated for USDC on Curve
- Operation 3: Provide liquidity to the DAI-USDC pool on Uniswap
The limit of transactions that can be executed in a single transaction is limited only by the gas limit, i.e. the maximum payable gas per transaction. In fact, every transaction requires the payment of gas, even if it fails.
Gas
The price required to successfully conduct a transaction or execute a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain. It’s a bit like paying for petrol to be able to take a trip.
The same thing happens with flash loans, a feature first developed by Aave that uses smart contracts to regulate this complex transaction.
Flash loans are loans that have to be generated and settled in the same transaction, within the same blockchain block.
So there is no risk that the borrower will not pay the loan, but there is a risk associated with flaws in the smart contracts that enable the flash loan.
The main advantage is that they do not require the payment of any collateral, but only a 0.09% fee.
Flash loan use cases
Flash loans are currently mostly accessible to developers with trading skills and DeFi experts, but there are protocols such as Furucombo, Defi Saver and Collateral Swap that allow even non-programmers to use them.
However, their use is associated with advanced strategies, including arbitrage and the use of DeFi lending protocols.
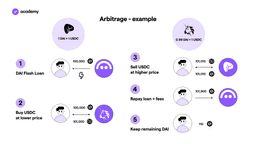
Arbitrage with Flash loans
Arbitrage means making a series of rapid trades, usually for a large amount, on different markets, leveraging the price differences to make a profit.
For example, a trader may buy at a lower price on one exchange and then sell at a higher price on another exchange.
In DeFi, this can also be done on Decentralised Exchanges.
For example, let’s imagine that DAI has a slightly lower cost on Curve than on Uniswap.
It is possible to exploit this to earn DAI, however arbitrage can only be profitable by using a large amount of capital.
Since few people have this kind of DAI, or money in general, it is easier to borrow DAI with a flash loan.
Then they will be used to buy USDCs on, say, Curve at a “discounted” price. And the USDCs will be redeemed for DAIs on Uniswap, at a higher price and therefore more profitable to sell.
You will then have to repay DAI’s flash loan in the same transaction, also paying the fees. Therefore the capital and the price difference must be high enough to be profitable even considering the fee and possible gas.
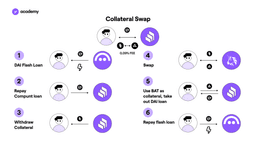
Collateral swap and Self-liquidation with Flash loans
Let us now turn to the context of decentralised lending, provided for example by Aave or Compound.
Usually a DeFi loan requires depositing a collateral to act as security and paying a periodic interest.
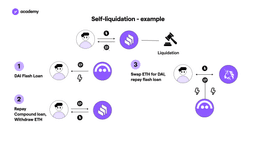
This can lead to various situations where it is convenient to self-liquidate one’s loan:
- If the interest rate has risen too high
- If the price of your collateral has dropped too much and you cannot put in more cash to secure the loan, but prefer to cancel it and avoid the protocol penalty
- If you want to sell the collateral for a profit, having already spent the loan
Or you may wish to swap the collateral with another if it has more advantageous interest rates.
What to look out for
First of all, as these are complex transactions, the costs of Ethereum or the blockchain in use must be considered. The total calculation of costs and gains must therefore take into account the current gas price and any fluctuations.
Slippage is another risk when executing an arbitrage or swap order. Remember that it depends on the liquidity of the protocol in use and the size of your order.
Slippage
The difference between the execution price of an order and the price entered in the order. It occurs when there is a lack of liquidity or market volatility.
The most unpredictable factor is front running. It is possible that someone else discovers the same arbitrage opportunity as you and manages to get their transaction validated before you do, due to timing or by paying additional gas fees. Front runners are usually bots dedicated to this purpose, or insiders with advantageous knowledge.
Flash loans have also been used for the most recent hacks on certain DeFi protocols, which have been strengthened in response.
Although flash loans are currently only usable with high technical skills, by working on their risks and usability they could be exploited by everyone via dapps and become a unique DeFi tool.