Ripple: the bank-favored cryptocurrency
November 19, 2020
8 min

Ripple is a blockchain technology that aims to bring speed and global reach to banks. It has been working with traditional financial systems for over a decade, collaborating with financial institutions to improve the system from within.
Many institutions, including Santander, Western Union, and American Express, have adopted Ripple solutions to simplify payments and reduce transaction costs, especially across borders.
As a result, they can offer their customers more convenient payment solutions and gain a competitive advantage over their competitors. Ripple’s mission is to provide a decentralised payment system that banks can use to improve their services.
In 2023, Ripple won a significant regulatory victory in its lawsuit against the Security and Exchange Commission (SEC). As a result, XRP was officially declared not to be a security, generating excitement throughout the cryptocurrency industry.
Fun fact
The Ripple platform was created by Ryan Fugger in 2004, who had been working on a local exchange trading system in Vancouver.
The XRP Ledger
Ledger XRP (XRPL) is a decentralised, public ledger that allows anyone to participate. The XRP Ledger facilitates assets denominated in traditional currencies like dollars and euros and includes a decentralised exchange as part of its protocol.
It differs from the main blockchain in the use of three elements:
- Gateways are used to transfer non-native assets on the XRP ledger and are commonly used by banks on RippleNet.
- An Issuance allows a single user to ‘lock’ any asset on the ledger, which can then be sent to other accounts on the ledger.
- Trust lines are required to make Issuance transactions secure. Unlike XRP, which can be sent to anyone, an Issuance can only be sent to parties agreeing to open a trust line. While I can send and receive XRP from anyone in the world, I can only send an Issuance of the dollars I claim to have to accounts that trust my word.
Validation
The nodes of the XRP Ledger are known as Validators. Their primary function is to validate transactions by casting their vote. While anyone can become a Validator, not all are selected to validate transactions. To select validators, users must create a unique node list (UNL) of other users they trust. However, Ripple also provides a standard list of validators that users can choose from.
Consent
The XRP Ledger Consensus Protocol, or RPCA, is a unique consensus protocol used by the Ledger. This protocol enables the Ledger to continue functioning even if some nodes in the network behave inappropriately or become unreachable.
In case too many participants are misbehaving or unreachable, the network stops making progress instead of confirming invalid transactions or changing its rules. This property of the network’s ability to function even with disturbing elements is called Byzantine Fault Tolerance. Further discussion on this topic can be found at the end of the text.
RippleNet
Let’s explore RippleNet, a distributed network that aims to connect all banks worldwide and provide a secure method for sending money between them. International money transfers can be complex and involve multiple currency and institution transfers, resulting in high service fees.
RippleNet is built on the XRP Ledger and is a closed network of institutions with contracts with Ripple. Transactions on RippleNet are private and only accessible to these institutions.
Initially, Ripple’s idea was to create a payment network to facilitate instant payments with different digital assets. This is now referred to as On-Demand Liquidity. Customers such as MoneyGram, TransferGo, mercuryFX, and GoLance use RippleNet with ODL to process their payments instantly (in less than two minutes) using XRP as the payment medium.
What is XRP?
XRP is the native cryptocurrency of Ripple, and it operates differently than other coins in the market. It is not mined periodically, and it is divisible into six decimal places, with the smallest unit called a drop.
1 XRP = 1 million Drop
Unlike most other coins on the market, it is not mined periodically. Currently, over 54 billion XRP are in circulation (as of February 2024), and the maximum supply is 100 billion.
To understand how Ripple works, it’s important to note that transaction fees paid by the user in XRP are destroyed, known as ‘coin burn’. This process removes XRP coins from circulation, making it a scarce and inflation-resistant cryptocurrency.
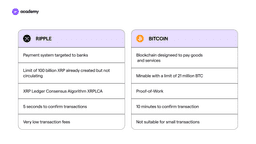
Differences between Bitcoin and Ripple XRP
Advantages
- Speed: XRP transactions are verified in 4 seconds, compared to 10 minutes for Bitcoin.
- Scalability: XRP consistently handles 1,500 transactions per second (TPS), 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and can be scaled up to handle the same transaction volume as Visa.
- Environmentally friendly: The XRP Ledger instantly settles XRP transactions without the energy costs associated with Proof of Work (or mining).
The SEC’s legal action and Ripple’s victory
One of the unique characteristics of this project is the challenging relationship Ripple has had with the SEC, the regulatory body responsible for financial markets in the United States, since 2020. It is only possible to explain what Ripple is by mentioning the legal issues it has faced.
On December 12, 2020, Ripple hosted the Spark token airdrop (FLR), in which FLRs were distributed based on the amount of XRP held in wallets that supported the airdrop. The event was an additional incentive to hold or purchase XRP until December.
However, just a few days later, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Ripple Labs, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency. The lawsuit claimed that XRP was, in fact, a security token.
The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) claimed that the company’s founders sold XRP as a share in Ripple without registering it. The ICO that launched XRP raised over $1.3 billion from investors worldwide.
The SEC’s lawsuit argued that Ripple did not register its offering as an investment contract for investors. Ripple responded to the lawsuit on Twitter. As a result of this legal action, some of the major exchanges delisted XRP, and Ripple’s value plummeted.
There has been much debate about whether Ripple is a security or not. On July 13, 2023, a New York District Judge named Analisa Torres ruled favour of Ripple against the SEC. This ruling implies that Ripple is currently not classified as a security, although the US government agency could still appeal.
Insight: The Problem of the Byzantine Generals
To fully understand Ripple and its operations, it’s essential to address the Byzantine Generals problem and its relation to the consensus protocol of Ripple networks. The consensus protocol of Ripple networks is based on the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) model, which is widely used in the industry.
The Byzantine Fault Tolerance of a blockchain is derived from the problem of Byzantine Generals, which is well-known in the field of logic. The problem aims to enable generals to decide on their next move unanimously.
Here are the conditions:
- There are four Byzantine generals, each with his army, surrounding a fortress
- They have two options: attack or retreat
- The decision must be unanimous, and the move must be coordinated.
- Once they have voted on the decision, they cannot change their minds
- They can send messages to each other to communicate the decision
The primary hurdle in resolving a situation is the possibility of lost messages or single or multiple generals sending out false or misleading information. A Byzantine Fault Tolerant system can function normally even if a network participant is acting maliciously or unwilling to participate. Applying blockchain technology can significantly reduce the time it takes to verify transactions.